What is git?
Open source and free Source Control Management – SCM. You can manage changes to files over time. Download for your system. Use gitbash to control. Other command line tools can be used.
Configure git
Specify name and email address – so git knows who is doing stuff
git config --global user.name “Your Name”
git config --global user.email <your email>
Specify default branch name – (this was done in the installation too)
git config –global init.default branch main
Initialise Repository
cd c:/<file location>
cd c:/users/BADASS/Onedrive/Documents/git_experiment (for example)
git init
there will now be a hidden file in the folder – .git
git Status
git status
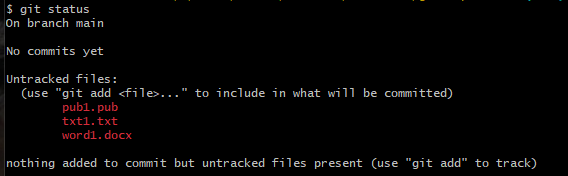
All the files are untracked
Track a File
git add <filename>
git add word1.docx (for example)
git add –all
git add -A (another way of tracking all)
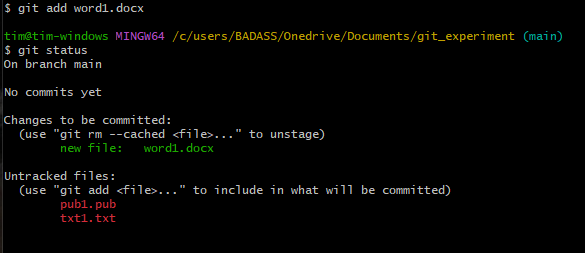
Unstage a file (stop tracking)
git rm --cached <filename>
git rm --cached word1.docx (for example)
Ignore files
- create new text file called .ignore
- insert files you want to ignore
Commit
Takes a snapshot of the repository
git commit -m “message”
Changes to files
If you change a file git will recognise this
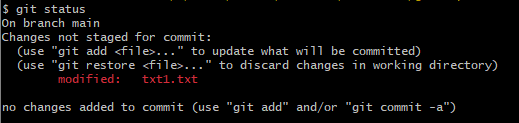
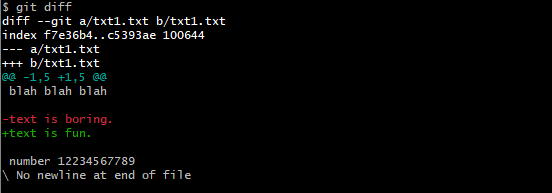
git diff
To see the difference
Environments
- Working Files
- Staging
- Commit
Add/remove modified file to ‘snapshot’
git add txt1.txt
Places this file into Staging where it will stay until we are ready to commit
git restore --staged txt1.txt
This will remove the file from Staging
Bypass Staging
git commit -a
Commits all
Restore a file
You could delete a file from the folder and then git status would show
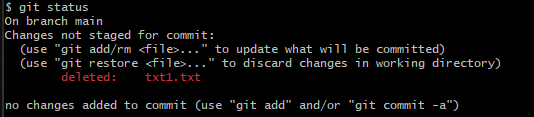
We can then restore this file with
git restore txt1.txt
Change filename
Use mv
git mv “txt1.txt” “txt2.txt”
git Log
git log
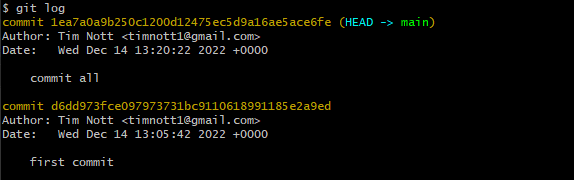
git log --oneline
Amend Commit
git commit -m ”message” –amend
Reset to Previous Commit
git reset 1ea7a0a
Rebase
git rebase -I --root
Branches
- A copy of your main branch which you can edit and then merge once you are satisfied with the changes
- Used a lot in coding development
Create New Branch
git branch fixbug
creates new branch
git branch
shows branches
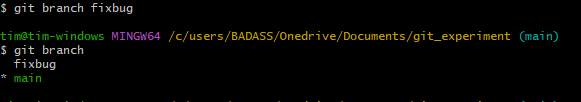
git switch fixbug
switches to this branch
Merge branches
git merge -m “merge fixbug with main” fixbug
Delete Branch
git branch -d fixbug
Merge Conflicts
- if you change the main branch whilst the fixbug branch is also edited you encounter a conflict when you try and merge them
Set Up github Account
- https://github.com/
- Sign up – usual process
Create Cloud Repo
- Create a new repository
- Give it a name
- Public/Private – depends on who you are working with
- Create repository
Push Existing Repo
We already have a repository on our local computer. github gives it the commands for pushing it to the cloud.
git remote add origin https://github.com/ChronikDog/Repo_1.git
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
go to github and see the files synced to the cloud.
Leave a Reply