Real-time network performance insights. This powerful command-line tool is an indispensable asset for system and network administrators aiming to keep a vigilant eye on TCP/IP connections and network bandwidth utilization.

What is iftop?
iftop, short for ‘interface top’, functions akin to the well-known Linux utility ‘top’, but with a focus on network activity. It provides a dynamic view of the data flowing through an interface, displaying bandwidth usage on a per-connection basis. This immediate feedback allows users to identify which hosts are consuming the most bandwidth, a crucial aspect in managing network resources efficiently and mitigating potential bottlenecks.
Key Features and Benefits
One of the core strengths of iftop is its simplicity and ease of use. By running a single command, users can observe the incoming and outgoing traffic from and to different hosts. The tool displays information such as the source and destination addresses, the current bandwidth usage, and the total data transferred over a specific period. This visibility is pivotal for troubleshooting network issues, planning bandwidth allocation, and ensuring that critical services have the necessary resources to operate smoothly.
Moreover, iftop offers several customization options to tailor its output to specific needs. Users can filter traffic by port or IP address, view bandwidth usage by network interface, and even display the network activity graphically in a terminal. These features make iftop a versatile tool that can adapt to various network analysis scenarios.
Getting Started with iftop
Installing iftop is straightforward on most Linux distributions.
For Debian-based systems:
sudo apt-get install iftop
Red hat-based distributions:
yum install iftop
Once installed, running iftop is as simple as typing iftop in the terminal. For a more detailed view, users can employ flags such as -i to specify an interface or -n to prevent hostname resolution, enhancing the tool’s performance.
Conclusion
Exploring iftop: The Must-Have Network Monitoring Tool for Linux
In the bustling world of network administration, Linux users are constantly in search of efficient tools to monitor network traffic and bandwidth usage. Amid a plethora of options, iftop emerges as a standout choice for those seeking real-time network performance insights. This powerful command-line tool is an indispensable asset for system and network administrators aiming to keep a vigilant eye on TCP/IP connections and network bandwidth utilization.
What is iftop?
iftop, short for ‘interface top’, functions akin to the well-known Linux utility ‘top’, but with a focus on network activity. It provides a dynamic view of the data flowing through an interface, displaying bandwidth usage on a per-connection basis. This immediate feedback allows users to identify which hosts are consuming the most bandwidth, a crucial aspect in managing network resources efficiently and mitigating potential bottlenecks.
Key Features and Benefits
One of the core strengths of iftop is its simplicity and ease of use. By running a single command, users can observe the incoming and outgoing traffic from and to different hosts. The tool displays information such as the source and destination addresses, the current bandwidth usage, and the total data transferred over a specific period. This visibility is pivotal for troubleshooting network issues, planning bandwidth allocation, and ensuring that critical services have the necessary resources to operate smoothly.
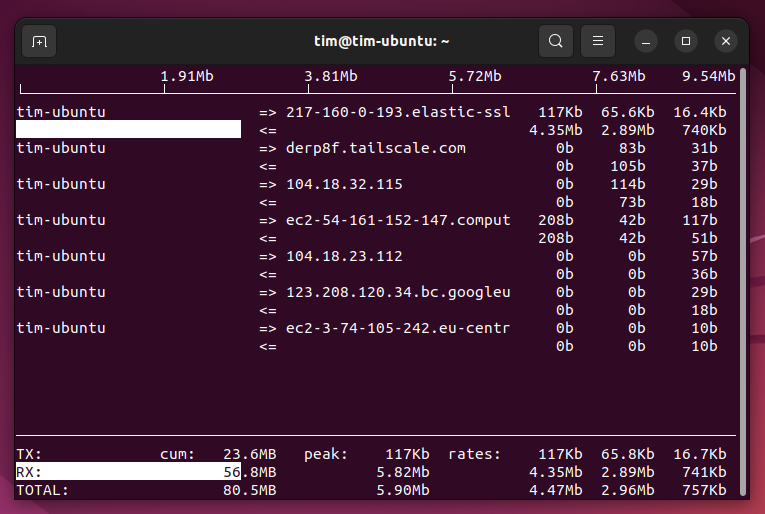
Moreover, iftop offers several customization options to tailor its output to specific needs. Users can filter traffic by port or IP address, view bandwidth usage by network interface, and even display the network activity graphically in a terminal. These features make iftop a versatile tool that can adapt to various network analysis scenarios.
Getting Started with iftop
Installing iftop is straightforward on most Linux distributions. For Debian-based systems, one can install it using apt-get install iftop, while yum install iftop will suffice for Red Hat-based distributions. Once installed, running iftop is as simple as typing iftop in the terminal. For a more detailed view, users can employ flags such as -i to specify an interface or -n to prevent hostname resolution, enhancing the tool’s performance.
Conclusion
For Linux users tasked with monitoring and managing network traffic, iftop is a tool that combines power with simplicity. Its real-time monitoring capabilities provide immediate insights into network performance, making it easier to identify and address issues proactively. Whether you’re a seasoned network administrator or just starting out, iftop is a valuable addition to your toolkit, offering a clear window into the dynamics of your network traffic.