
Creating a shared folder on a Linux machine and accessing it from Windows machines on the same network involves setting up Samba on the Linux machine and configuring the Windows machine to access the shared folder. This is because Linux doesn’t have Server Message Block(SMB) natively.
Here is a step-by-step procedure:
Install Samba on the Linux machine
Open a terminal window.
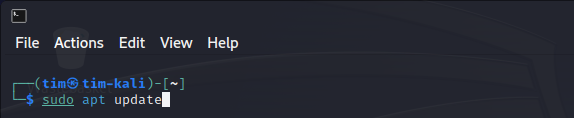
Update the package list by running:
sudo apt update
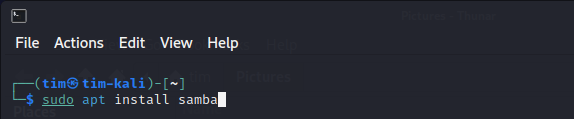
Install Samba by running:
sudo apt install samba
Create a shared folder
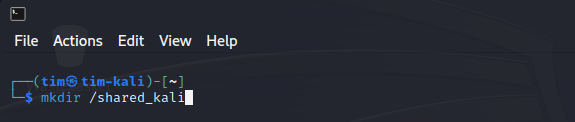
In the terminal, create a new directory for sharing:
mkdir /path/to/shared/folder
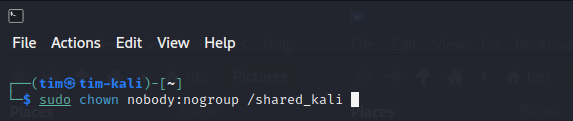
Change the ownership of the shared folder to the ‘nobody’ user and ‘nogroup’ group:
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /path/to/shared/folder
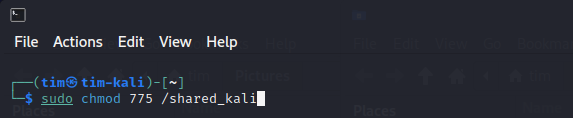
Set the appropriate permissions:
sudo chmod 775 /path/to/shared/folder
Configure Samba
Create a backup of the original Samba configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.bak
Linux to windows network share with samba
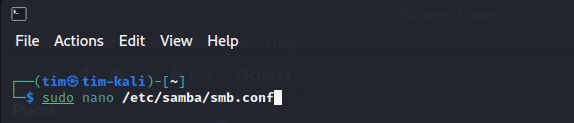
Open the Samba configuration file in a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
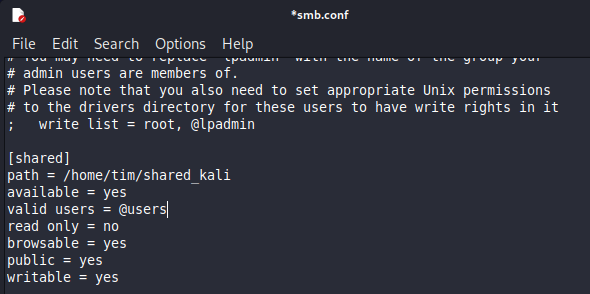
Add the following configuration block to the end of the file:
[SharedFolder]
path = /path/to/shared/folder
available = yes
valid users = @users
read only = no
browsable = yes
public = yes
writable = yes
Replace ‘SharedFolder’ with the name for your shared folder and /path/to/shared/folder with the path of the shared folder.
Save the changes and exit the text editor (Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter in nano).
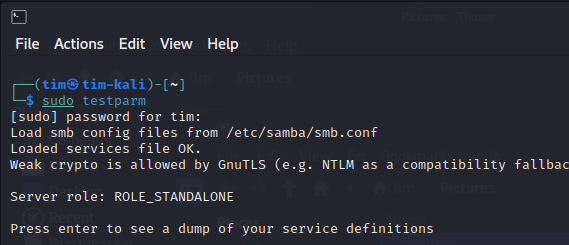
Test the Samba configuration for any syntax errors:
sudo testparm
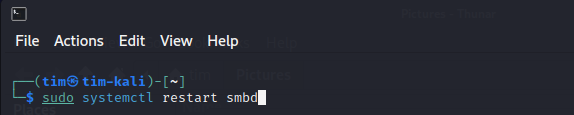
Restart the Samba service:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
Configure the firewall (optional, if using a firewall)
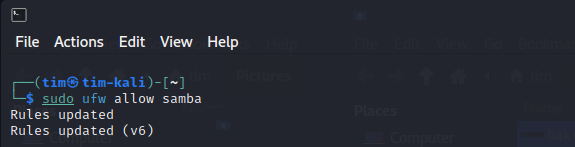
Allow samba through the firewall:
sudo ufw allow samba
Enable the firewall, if not already enabled:
sudo ufw enable
Access the shared folder from a Windows machine
On the Windows machine, open File Explorer.
Click in the path field near the top.
Enter:
\\<ip address of Linux machine>\<name of shared folder>
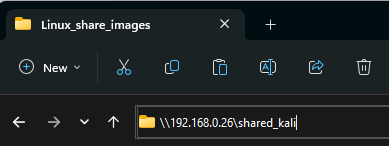
Press Enter
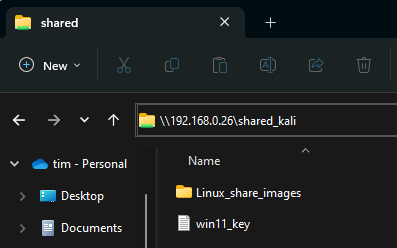
Enter the Linux machine’s ‘nobody’ user credentials, if prompted (the password is typically left blank).
You should now be able to access the shared folder on the Linux machine from the Windows machines on the same network.
In conclusion, sharing files between Linux and Windows machines is a crucial aspect of working in a multi-platform environment. By following the steps provided in this guide, you can seamlessly set up a shared folder on your Linux machine and access it from Windows machines on the same network. Samba serves as an effective bridge between these two operating systems, enabling smooth file sharing and collaboration. With a properly configured shared folder, you can enjoy the benefits of cross-platform collaboration and improve the overall efficiency of your network.
