How to create a very simple weather app in Python. In this tutorial, we will use the requests module to retrieve weather data from the OpenWeatherMap API and the tkinter module to build a simple GUI for our weather app.
Let’s get started!

Step 1: Setting up the environment.
First, we need to set up the environment for our project. We will be using Python 3, so make sure you have it installed on your computer. You can download it from the official website here.
Next, we need to install the requests module. To do this, open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install requests
We also need to install the tkinter module. If you’re using Python 3 on Windows or macOS, this should be installed by default. If you’re using a Linux distribution, you may need to install it separately. For example, on Ubuntu, you can install it by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install python3-tk
If you use an IDE such as Pycharm then it will give you the option of installing modules that you attempt to use but haven’t yet installed. Very handy.
Step 2: Register for OpenWeatherMap API Key.
Next, we need to register for an API key with OpenWeatherMap. To do this, go to their website here and create an account. Once you’ve created an account, log in and go to your API keys page. Create a new API key and copy it to your clipboard.
Step 3: Writing the code.
Now that we have everything set up, let’s start writing our code.
We’ll start by importing the necessary modules and defining a function to retrieve weather data from the OpenWeatherMap API.

In this function, we specify the API endpoint and API key for OpenWeatherMap, and the location for which we want to retrieve weather data. We make a GET request to the API with these parameters, and check the status code of the response to make sure it was successful. If it was, we return the weather data as a JSON object. If not, we print an error message and return None.
Next, we’ll create a window for our weather app using the tkinter module.

In this code, we create a new window with the title “Weather App”. We then create a label with the text “Enter Location:” and an entry widget for the user to input the location they want to retrieve weather data for.
We also create a button labelled “Submit” which will call the get_weather function with the location entered by the user.
Finally, we create a label to display the weather data retrieved from the API. We can now define the get_weather function to update the weather label with the current temperature for the given location.
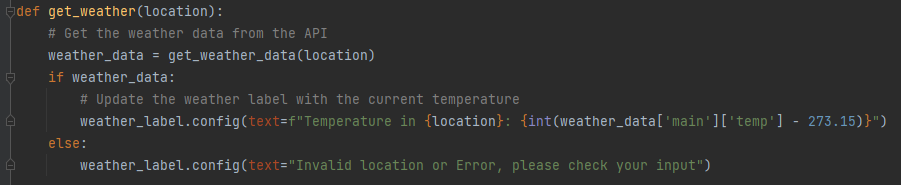
In this function, we call the get_weather_data function to retrieve weather data for the given location. If the function returns weather data, we update the weather label with the current temperature for that location.
We subtract 273.15 from the temperature value to convert it from Kelvin to Celsius. If the get_weather_data function returns None, we update the weather label with an error message.
Finally, we run the main loop of the tkinter application.
root.mainloop()
This will start the application and display the window we created.
Step 4: Putting it all together.
Now that we’ve written all the necessary code, put it all together in the order we have here.
Make sure you replace YOUR_API_KEY_HERE with the API key provided from OpenWeatherMap.
Once you have done that it is time to run the code!
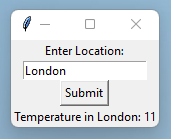
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve learned how to use the requests and tkinter modules in Python to create a weather app. We’ve used the OpenWeatherMap API to retrieve weather data for a specified location and displayed the current temperature in Celsius using a GUI built with tkinter. This is just a basic implementation and there’s a lot more that could be done to improve the app. For example, we could add more weather information, allow the user to specify units, or even display a forecast for the next few days.
I hope this tutorial was helpful and you were able to create your own weather app.